How To Setup Openldap Server For Mac Osx
Setup local LDAP server in mac OSX. Setting up OpenLDAP under MAC OS X – Akalanka Sep 28 '15 at 3:50. Add a comment 3 Answers active oldest votes.
Time This lesson takes approximately 2 hours to complete. Goals Understand how data is structured and how entries are distinguished in an LDAP database Use command-line and GUI tools to search for a specific entries in a given LDAP database Use Directory Access to add a Mac OS X server providing directory services for user authentication Troubleshoot problems with Open Directory records retrieved from an LDAP database Interpret entries in a network user account to determine why a user is unable to log in correctly Data is valuable only if it can be stored and accessed. With multiple vendors of directory services solutions competing for your business, you may worry that their disparate systems will not be able to interoperate and that it will be difficult for clients to support multiple vendors. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol ( LDAP) addresses these concerns by providing a protocol that all vendors can support while still being able to differentiate themselves on the basis of additional features, over and above what a simple data access protocol dictates. This lesson introduces you to the LDAP specification and explains Mac OS X support for this nearly universal protocol. In Lesson 2, “Accessing Local Directory Services,” you saw how Open Directory provides a means of retrieving information from a local data store to identify and authenticate user accounts on the local computer. Now you’ll learn how to request and retrieve identification information stored in an LDAP directory on the network, in particular, the LDAP directory on Mac OS X Server.
By accessing the directory in Mac OS X Server on your network, you can take advantage of features such as automounting share points, preferences management, and mobile user accounts. Understanding LDAP LDAP is an industry-standard method of accessing data from within a directory. If your organization already has a network directory service in place, it is likely that the directory is based on LDAP or is accessible via LDAP. LDAP is many things, and can be described in different ways. It is: • An information model.
It defines how data is accessed. • A namespace. It defines how to distinguish one piece of data from another, similar to a URL. • A protocol. It defines how a client can read, write, and search for data.
My passport for mac hhd or ssd?. Western Digital WD 2TB My Passport for Mac Portable Hard Drive for $99 - Compare prices of 5733 products in Solid State Drive (SSD) from 84 Online Stores in Australia. Save with MyShopping.com.au! SSD-based Mac computers are great, but sometimes you need more space for your ever-growing iTunes and Photos collections. With the My Passport for Mac drive connected to your Mac, you can add up to 4TB of space for your favorite music and photos.
• A distribution model. LDAPv3 defines how to distribute the logical information model physically.
This means that data can be partitioned and stored on multiple hosts, while still being one logical directory. More Info The distribution model aspect of LDAP is not covered in this book. Please refer to the References section at the end of this lesson for more information.
• A way to standardize access to directory data, regardless of how or where that data is stored. This standardization, while simple in in concept, is quite complex in implementation, requiring standardized naming (the namespace) and standardized searching. • Extensible. It can be customized to fit any organization’s directory services needs. LDAP Information Model The basic unit of LDAP is an entry, or an instance of related attributes. It consists of one or more attributes and the values for those attributes in the following format: attribute=value LDAP uses the schema to define attributes, among other things. An object class specifies which attributes are required when populating the LDAP directory and which attributes will be allowed when populating the LDAP directory.
Use the links on this page to download the latest version of Coprocessor drivers. All drivers available for download have been scanned by antivirus program. After you upgraded your system to Windows 10 from Windows 7 or Windows 8, you might find your computer run slowly. Then you checked for the driver status in Device Manager, and saw a device named Coprocessor with a yellow exclamation mark next to it. You have no idea what the device is and how to remove the yellow mark. Home / How to, Software / Windows 10 Coprocessor driver missing. Previous Next. View Larger Image; Windows 10 Coprocessor driver missing. Installed Windows 10 x64 on Presario cq60-212em Coprocessor driver was missing in device manager Driver details: Hardware IDs. I currently have the SM Bus controller driver missing or not installed.Coprocessor driver missing or not installed and blue tooth peripheral driver missing or not installed. Using update it indicates it can not find any driver. I a using Mac OS 10.6.3 – 13″ Macbookpro 7.1 core 2 duo 2.66 GHz,p8800 4 gig ram 1066 MGz L2 Cache Boot camp 3. 
This attribute definition provides data integrity. Object classes are defined in the schema. Because LDAP is so customizable, the schema can be tailored to meet the needs of many different deployments. The attributes are usually an abbreviation or mnemonic for a typical characteristic.
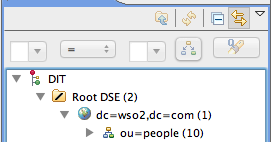
For instance, dc stands for domain component and cn stands for common name. These abbreviations can be used in several locations within the tree and may not be specific to each entry within each entry. LDAP Namespace Because the structure of an LDAP directory can be different at each site, you have to tell any LDAP client where to find an entry.
To request a particular entry, the client uses the logical path to the entry or the distinguished name (dn). This is similar to an absolute path in the Mac OS X file system. Here is an example of the dn for Warren Peece: dn:uidNumber=501,cn=users,dc=mainserver,dc=pretendco,dc=com The structure of the LDAP hierarchy is defined by the distinguished names. In addition, one or more attributes in an entry can be used as the name of the entry itself. This is the entry’s relative distinguished name (rdn), which is similar to a relative path in the Mac OS X file system. For example rdn:uidNumber=501 refers to all the attribute/value pairs in that entry.